
This Top 10 list brings you some of the most famous scientists throughout history:
10 Max Planck
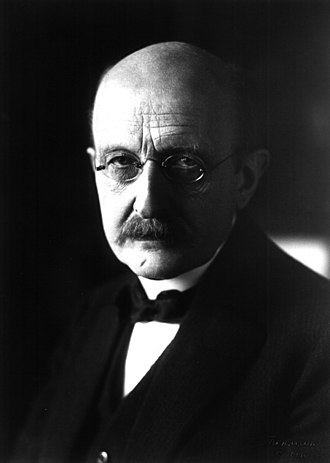
Max Planck was born on April 23, 1858 in Kiel, Germany and died on October 4, 1947 in Göttingen, Germany. He is widely regarded as one of the most important theoretical physicists of the 20th century, and is famous for his pioneering work in the field of quantum mechanics.
- Planck initially studied physics and mathematics at the University of Munich, but switched to theoretical physics after attending a lecture by Ludwig Boltzmann.
- In 1900, Planck proposed the idea of quantized energy, which eventually led to the development of quantum mechanics.
- In 1918, Planck was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the theory of heat radiation.
- Planck was a strong advocate for the unity of science, and believed that all natural phenomena could be explained by a single set of laws.
- He was an early supporter of Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
- He was a professor of Theoretical Physics at the University of Berlin, and later at the University of Frankfurt.
- His son Erwin Planck was a chemist
- He was a member of the Prussian Academy of Sciences, the German Academy of Sciences Leopoldina and the Berlin Academy of Sciences
- He was also a member of the Bavarian Academy of Sciences and Humanities
- He was a member of the Order Pour le Mérite and the Nobel laureate.
9. James Clerk Maxwell

James Clerk Maxwell was born on June 13, 1831 in Edinburgh, Scotland, and died on November 5, 1879 in Cambridge, England. He is considered one of the greatest scientists in history, and is famous for his groundbreaking work in electromagnetism.
- Maxwell was a child prodigy, and had a deep understanding of mathematics and physics from a very young age.
- He was a professor of natural philosophy at Marischal College in Aberdeen, and later at King’s College in London.
- In 1856, he published a paper on the nature of color, in which he proposed that color is a physical property of light, and not a property of the object being viewed.
- In 1861, Maxwell published his famous paper “On Physical Lines of Force” in which he formulated the four Maxwell’s equations that describe the behavior of electric and magnetic fields.
- In 1864, he published “A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field” where he proposed that light is an electromagnetic wave.
- Maxwell’s equations are considered one of the great milestones in the history of science, and laid the foundation for the development of the modern theory of electromagnetism.
- He was a Fellow of the Royal Society and a member of the Royal Society of Edinburgh
- Maxwell’s work on the kinetic theory of gases laid the foundation for statistical mechanics
- He was also involved in the development of the color photograph, and is considered one of the founders of the field of color science.
- Maxwell’s work on the nature of light had a profound influence on the development of quantum mechanics, and his ideas were later developed by Einstein in his theory of special relativity.
8. Stephen Hawking

Stephen Hawking was born on January 8, 1942 in Oxford, England, and passed away on March 14, 2018 in Cambridge, England. He is considered one of the greatest scientists of the 20th century and is famous for his groundbreaking work on black holes and the origins of the universe.
- Stephen Hawking was diagnosed with ALS (Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) at the age of 21, and was given only a few years to live, but he lived for more than five decades with the disease.
- He was a theoretical physicist and cosmologist, and was the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at the University of Cambridge for 30 years.
- In 1974, he proposed the four laws of black hole mechanics, which describes the behavior of black holes and laid the foundation for the study of black hole thermodynamics.
- He proposed that black holes emit radiation, now known as Hawking radiation.
- He wrote several bestselling books, including “A Brief History of Time” which has sold over 10 million copies.
- He was a proponent of the “no boundary” theory of the universe, which suggests that the universe has no beginning or end.
- He was the director of research at the Centre for Theoretical Cosmology at the University of Cambridge.
- He was a Fellow of the Royal Society, a member of the US National Academy of Sciences, and a recipient of the Presidential Medal of Freedom.
- He was also a vocal advocate for the importance of science education, and for the rights of people with disabilities.
- He appeared in several television shows, including “The Big Bang Theory” and “Star Trek: The Next Generation”. He was also the subject of a biographical film, “The Theory of Everything,” which was released in 2014.
7. Thomas Edison

Thomas Edison was born on February 11, 1847 in Milan, Ohio, and passed away on October 18, 1931 in West Orange, New Jersey. He is widely considered as one of the greatest inventors of all time and is famous for his contributions to the fields of electric power generation and mass communication.
- Edison was homeschooled by his mother, who was a teacher.
- Edison began his career as a telegraph operator and quickly became known for his ability to fix broken telegraph equipment.
- He established the first industrial research laboratory in Menlo Park, New Jersey, where he developed many of his most famous inventions, including the incandescent light bulb, the phonograph, and the motion picture camera.
- He was awarded over 1,000 patents in his lifetime, making him the most prolific inventor in American history.
- He was also involved in the development of the electric power industry, and helped establish the first electric utility company in 1882.
- He was a proponent of direct current (DC) electricity, but lost out to the alternating current (AC) system developed by George Westinghouse and Nikola Tesla.
- He was a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, the National Academy of Sciences, and the American Philosophical Society.
- He was a friend of the famous inventor and businessman Henry Ford and helped him in his early days of automobile manufacturing.
- He had a lifelong interest in mining and geology, and owned several mines throughout his life.
- He was also an advocate for education and supported the development of educational institutions, such as the Edison Institute of Technology (later known as Thomas A. Edison Technical School), which was established in Newark, New Jersey.
6. Marie Curie

Marie Curie was born on November 7, 1867 in Warsaw, Poland and died on July 4, 1934 in Passy, France. She is considered one of the most accomplished and renowned scientists of all time and is famous for her pioneering work in the fields of radioactivity and nuclear physics.
- Curie was the first woman to receive a Nobel Prize, and the first person to receive two Nobel Prizes in two different sciences (physics and chemistry).
- She was the first woman to become a professor at the University of Paris, and the first woman to be entombed on her own merits in the Panthéon in Paris.
- She discovered two new elements, polonium and radium, and coined the term “radioactivity”
- She co-developed the theory of radioactivity, and developed techniques for isolating radioactive isotopes, which led to the discovery of many other elements.
- She was a pioneer in the use of radioactive isotopes in medicine, and her work led to the development of new cancer treatments.
- She was a strong advocate for women’s rights, and was instrumental in the establishment of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
- She was a member of many scientific societies, including the French Academy of Sciences, the Royal Society of London, and the American Academy of Arts and Sciences.
- During World War I, she established mobile radiography units to provide X-rays to field hospitals, earning her the nickname “the angel of the battlefield”
- She was the first female Nobel laureate, and the first person to win two Nobel Prizes in different sciences.
- Her notebooks, which are still radioactive, are kept in lead-lined boxes and are handled with special precautions.
5. Nikola Tesla

Nikola Tesla was born on July 10, 1856 in Smiljan, Croatia and died on January 7, 1943 in New York City, United States. He was an inventor, electrical engineer, mechanical engineer, and futurist who made important contributions to the design of the modern alternating current (AC) electricity supply system.
- Tesla studied at the Austrian Polytechnic in Graz, Austria and later in Prague.
- He worked as an assistant to Thomas Edison, but the two had a falling out over their differing ideas about direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC) electricity.
- He is best known for his invention of the Tesla coil, which is still used in radio and television technology.
- He made significant contributions to the design of the modern alternating current (AC) electricity supply system.
- He held over 300 patents for his inventions and was known for his ideas of wireless communication, radio and X-rays.
- He proposed the existence of a “world wireless system” that would allow for the transmission of information and energy without wires.
- Tesla was a proponent of the wireless transmission of energy, and claimed to have built a device that could transmit energy wirelessly.
- He was a member of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers, the National Electric Light Association, and the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
- He suffered a nervous breakdown in 1899, which led to him becoming reclusive and focusing on more theoretical and visionary work
- Despite his contributions to the field of electrical engineering, Tesla died penniless and in relative obscurity.
4. Charles Darwin
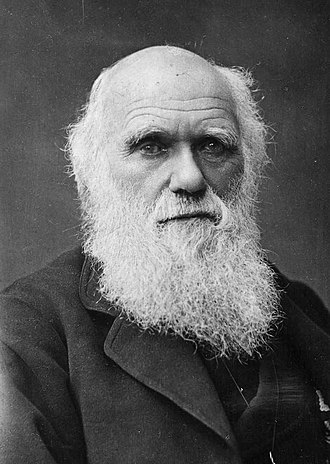
Charles Darwin was born on February 12, 1809 in Shrewsbury, England and died on April 19, 1882 in Downe, Kent, England. He is considered one of the most influential scientists of all time and is famous for his theory of evolution through natural selection.
- Darwin studied at the University of Edinburgh and later at the University of Cambridge.
- He is best known for his theory of evolution through natural selection, which was first presented in his book “On the Origin of Species” in 1859.
- He proposed that species evolved over time through the process of natural selection, where those best adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and pass on their traits to their offspring.
- He also proposed that all life on Earth is related through common ancestry, and that the diversity of life is the result of the gradual accumulation of small changes over millions of years.
- He made important contributions to the study of geology and natural history, and was the first to propose that coral reefs were formed by the accumulation of the skeletons of marine organisms over time.
- He was a naturalist and natural historian, and made many scientific expeditions, including a five-year trip around the world on the HMS Beagle.
- He was a member of the Royal Society, the Geological Society of London, and the Linnean Society.
- His work was controversial in his time, and it took years for his ideas to be accepted by the scientific community.
- He was a devout Christian and struggled with how to reconcile his religious beliefs with his scientific findings.
- He wrote many books, including “The Descent of Man” and “The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals”, which expanded on his theory of evolution and its implications for human behavior and emotions.
3. Galileo Galilei

Galileo Galilei was born on February 15, 1564 in Pisa, Italy, and died on January 8, 1642 in Arcetri, Italy. He is considered one of the most important figures in the history of science and is famous for his pioneering work in the fields of physics, astronomy, and mathematics.
- Galileo studied at the University of Pisa and later at the University of Padua.
- He is best known for his use of the telescope to observe the sky and for his support of the heliocentric model of the solar system, which proposed that the Earth and other planets orbit around the sun.
- He discovered four moons orbiting Jupiter, observed the phases of Venus, and discovered sunspots.
- He was the first to use the telescope to make scientific observations, which revolutionized the field of astronomy.
- He was a strong advocate for the scientific method and believed that scientific theories should be tested and verified through experimentation and observation.
- He was a professor of mathematics at the University of Pisa and later at the University of Padua.
- His work was controversial in his time and was met with resistance from the Catholic Church, who considered his ideas to be heretical.
- He was placed under house arrest by the Catholic Church for the last nine years of his life for his support of the heliocentric model of the solar system.
- He wrote several books, including “Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems” and “Two New Sciences” which laid the foundation for the development of modern physics and mechanics.
- He was also an accomplished mathematician and made important contributions to the field of physics, including the development of the law of falling bodies and the principle of relativity.
2. Isaac Newton

Isaac Newton was born on December 25, 1642 in Lincolnshire, England, and died on March 20, 1727 in London, England. He is considered one of the most influential scientists of all time and is famous for his groundbreaking work in the fields of physics, mathematics, and astronomy.
- Newton studied at the University of Cambridge, where he developed the foundation of calculus and laid the groundwork for the development of modern physics.
- He is best known for his three laws of motion and the law of universal gravitation, which explained the motion of objects in the natural world and formed the basis of modern physics.
- He made important contributions to the field of optics and developed the reflecting telescope.
- He was a professor of mathematics at the University of Cambridge and later served as the president of the Royal Society.
- He was a devout Christian and believed that his scientific discoveries were in harmony with the teachings of the Bible.
- He wrote several books, including “Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica” (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), which is considered one of the most important scientific books of all time.
- He was a member of the Royal Society, the French Academy of Sciences and the Prussian Academy of Sciences.
- He had a rivalry with German mathematician and physicist Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, who is also credited with the invention of calculus.
- He was a private person and didn’t publish most of his work in his lifetime and it was only after his death that many of his discoveries were made public.
- He had a great impact on the scientific revolution and the way we understand the world today, many of his work has been the foundation of many of the scientific discoveries that followed.
1. Albert Einstein

Albert Einstein was born on March 14, 1879 in Ulm, Germany and died on April 18, 1955 in Princeton, New Jersey. He is considered one of the most important scientists of all time and is famous for his contributions to the fields of physics and mathematics, particularly his theory of general relativity and his famous equation, E=mc².
- Einstein studied at the Polytechnic School in Zurich, Switzerland and later at the University of Zurich.
- He is best known for his theory of general relativity, which proposed that gravity is not a force between masses, but rather a curvature of spacetime caused by the presence of mass and energy.
- He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921 for his work on the photoelectric effect, which provided the first experimental evidence for the quantization of energy.
- He was a professor of physics at the University of Berlin and later at the Prussian Academy of Sciences.
- He was a pacifist and an advocate for world peace, and was a member of the German League of Human Rights and the Emergency Peace Campaign.
- He wrote several books, including “Relativity: The Special and General Theory” and “Ideas and Opinions” which popularized his scientific ideas to a wider audience.
- He was a member of the Prussian Academy of Sciences, the Royal Society and the National Academy of Sciences.
- He had a great impact on the development of quantum mechanics and the understanding of atomic and subatomic particles.
- He was a vocal advocate for civil rights and was an early member of the NAACP.
- Einstein’s brain was preserved for scientific study after his death, and it has revealed that it had structural differences from a typical brain, particularly in the region responsible for mathematical ability.
The Top 10 list of Famous Scientists
- Albert Einstein
- Isaac Newton
- Galileo Galilei
- Charles Darwin
- Nikola Tesla
- Marie Curie
- Thomas Edison
- Stephen Hawking
- James Clerk Maxwell
- Max Planck
Please note that this is a list of famous scientists and the list is ever-changing and based on the popularity and influence of the scientists at the time of publication, and this list might not be the same in the future. There are many other scientists that have made important contributions to the field of science.
